In a binary tree, the root node is at depth 0, and children of each depth k node are at depth k+1.
Two nodes of a binary tree are cousins if they have the same depth, but have different parents.
We are given the root of a binary tree with unique values, and the values x and y of two different nodes in the tree.
Return true if and only if the nodes corresponding to the values x and y are cousins.
Example 1:
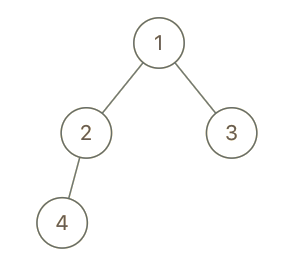
1
2
| Input: root = [1,2,3,4], x = 4, y = 3
Output: false
|
Example 2:
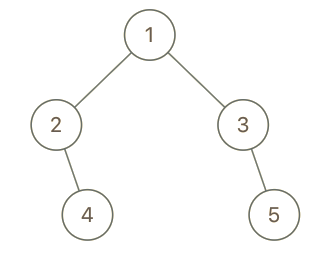
1
2
| Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4,null,5], x = 5, y = 4
Output: true
|
Example 3:

1
2
| Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4], x = 2, y = 3
Output: false
|
Solution:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isCousins(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {
int[] r = bfs(root, -1, x, 0);
int[] l = bfs(root, -1, y, 0);
return l[0] != r[0] && l[1] == r[1];
}
int[] bfs(TreeNode node, int parent, int value, int level) {
if (node.val == value) {
return new int[]{parent, level};
}
int[] result = new int[]{-1, -1};
if (node.left != null) {
result = bfs(node.left, node.val, value, level + 1);
}
if (result[0] != -1) {
return result;
}
if (node.right != null) {
result = bfs(node.right, node.val, value, level + 1);
}
if (result[0] != -1) {
return result;
}
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
}
|


