Given a list of lists of integers, nums, return all elements of nums in diagonal order as shown in the below images.
Example 1:
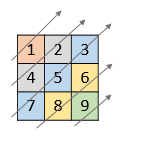
| |
Example 2:
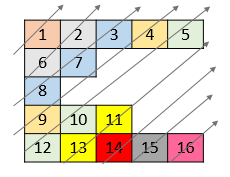
| |
Example 3:
| |
Example 4:
| |
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 10^5
- 1 <= nums[i].length <= 10^5
- 1 <= nums[i][j] <= 10^9
- There at most 10^5 elements in nums.
Solution:
| |