112. Path Sum
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return true if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals targetSum.
A leaf is a node with no children.
1
2
3
4
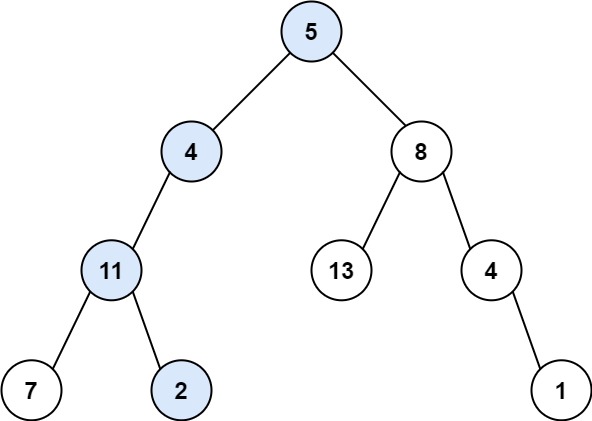
| Example 1:
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
Output: true
|
1
2
3
4
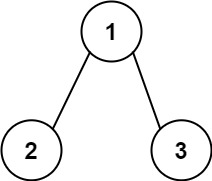
| Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
Output: false
|
1
2
3
4
| Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
Output: false
|
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 5000].
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
- -1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
List<TreeNode> q = new ArrayList<>();
q.add(root.left);
q.add(root.right);
while (q.size() > 1) {
TreeNode left = q.remove(0);
TreeNode right = q.remove(0);
if (left == null && left == right) {
continue;
}
if (left == null || right == null) {
return false;
}
if (left.val != right.val) {
return false;
}
q.add(left.left);
q.add(right.right);
q.add(left.right);
q.add(right.left);
}
return true;
}
public boolean isSymmetricRecursive(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
return isSymmetric(root.left, root.right);
}
boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
if (left == null && right == null) {
return true;
}
if (left == null || right == null) {
return false;
}
if (left.val != right.val) {
return false;
}
return isSymmetric(left.left, right.right)
&& isSymmetric(right.left, left.right);
}
}
|

