108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
Given an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
A height-balanced binary tree is a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than one.
1
2
3
4
5
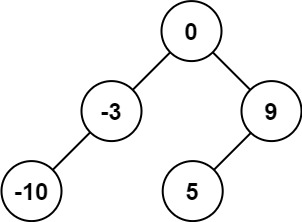
| Example 1:
Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
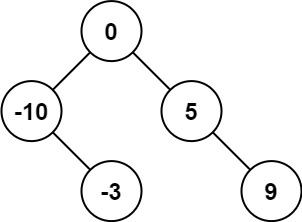
Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
Explanation: [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] is also accepted:
|
1
2
3
4
5
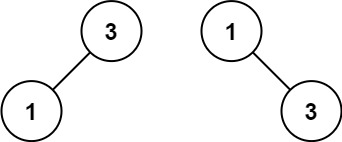
| Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,3]
Output: [3,1]
Explanation: [1,3] and [3,1] are both a height-balanced BSTs.
|
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 104
- -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
- nums is sorted in a strictly increasing order.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) return null;
return buildBST(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
TreeNode buildBST(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) {
if (hi < lo) {
return null;
}
TreeNode node = new TreeNode();
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
node.val = nums[mid];
node.left = buildBST(nums, lo, mid - 1);
node.right = buildBST(nums, mid + 1, hi);
return node;
}
}
|


