1557. Minimum Number of Vertices to Reach All Nodes
Given a directed acyclic graph, with n vertices numbered from 0 to n-1, and an array edges where edges[i] = [fromi, toi] represents a directed edge from node fromi to node toi.
Find the smallest set of vertices from which all nodes in the graph are reachable. It’s guaranteed that a unique solution exists.
Notice that you can return the vertices in any order.
1
2
3
4
5
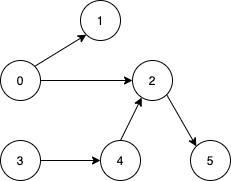
| Example 1:
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,5],[3,4],[4,2]]
Output: [0,3]
Explanation: It's not possible to reach all the nodes from a single vertex. From 0 we can reach [0,1,2,5]. From 3 we can reach [3,4,2,5]. So we output [0,3].
|
1
2
3
4
5
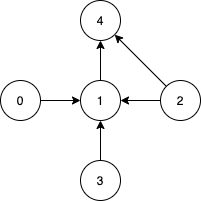
| Example 2:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[2,1],[3,1],[1,4],[2,4]]
Output: [0,2,3]
Explanation: Notice that vertices 0, 3 and 2 are not reachable from any other node, so we must include them. Also any of these vertices can reach nodes 1 and 4.
|
Constraints:
- 2 <= n <= 10^5
- 1 <= edges.length <= min(10^5, n * (n - 1) / 2)
- edges[i].length == 2
- 0 <= fromi, toi < n
- All pairs (fromi, toi) are distinct.
Solution#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class Solution {
public List<Integer> findSmallestSetOfVertices(int n, List<List<Integer>> edges) {
int[] indegree = new int[n];
for (var e: edges) {
indegree[e.get(1)]++;
}
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < indegree.length; i++) {
int v = indegree[i];
if (v == 0) {
res.add(i);
}
}
return res;
}
}
|

