2. Add Two Numbers
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
1
2
3
4
5
| Example 1:
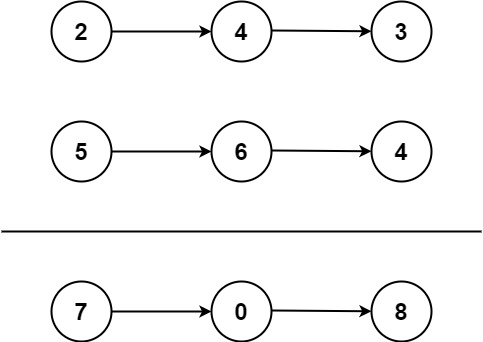
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
Output: [7,0,8]
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
|
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range [1, 100].
- 0 <= Node.val <= 9
- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
Solution#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = null;
ListNode curr = null;
ListNode prev = null;
int carry = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int value = 0;
if (l1 != null) value += l1.val;
if (l2 != null) value +=l2.val;
if (carry > 0) {
value+=1;
carry = 0;
}
if (value >= 10) {
carry = 1;
value = value % 10;
}
curr = new ListNode();
curr.val = value;
if (prev == null) {
prev = curr;
} else {
prev.next = curr;
prev = curr;
}
if (head == null) {
head = prev;
}
l1 = l1 != null? l1.next : null;
l2 = l2 != null ? l2.next: null;
}
if (carry > 0) {
prev.next = new ListNode(1);
}
return head;
}
}
|
Solution 1.08.2021#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
| /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
2 --- 4 --- 3
5 --- 6 --- 8
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy1 = l1;
ListNode dummy2 = l2;
ListNode res = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode head = res;
int add = 0;
while (dummy1 != null || dummy2 != null) {
int val1 = dummy1 != null ? dummy1.val: 0;
int val2 = dummy2 != null ? dummy2.val: 0;
int val = val1 + val2 + add;
if (val > 9) {
add = 1;
} else {
add = 0;
}
res.next = new ListNode(val % 10);
res = res.next;
if (dummy1 != null) {
dummy1 = dummy1.next;
}
if (dummy2 != null) {
dummy2 = dummy2.next;
}
}
if (add > 0) {
res.next = new ListNode(1);
res = res.next;
}
return head.next;
}
/*
null 1 2
prev -> curr -> next
*/
ListNode reverse(ListNode node) {
if (node == null) return null;
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = node;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
void print(ListNode node) {
ListNode curr = node;
while (curr != null) {
System.out.print(curr.val + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
|
