1168. Optimize Water Distribution in a Village
There are n houses in a village. We want to supply water for all the houses by building wells and laying pipes.
For each house i, we can either build a well inside it directly with cost wells[i - 1] (note the -1 due to 0-indexing), or pipe in water from another well to it. The costs to lay pipes between houses are given by the array pipes, where each pipes[j] = [house1j, house2j, costj] represents the cost to connect house1j and house2j together using a pipe. Connections are bidirectional.
Return the minimum total cost to supply water to all houses.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| Example 1:
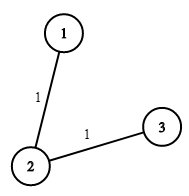
Input: n = 3, wells = [1,2,2], pipes = [[1,2,1],[2,3,1]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
The image shows the costs of connecting houses using pipes.
The best strategy is to build a well in the first house with cost 1 and connect the other houses to it with cost 2 so the total cost is 3.
|
Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 104
- wells.length == n
- 0 <= wells[i] <= 105
- 1 <= pipes.length <= 104
- pipes[j].length == 3
- 1 <= house1j, house2j <= n
- 0 <= costj <= 105
- house1j != house2j
Solution#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
| class Solution {
public int minCostToSupplyWater(int n, int[] wells, int[][] pipes) {
List<List<Integer>> edgeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < pipes.length; i++) {
int[] pipe = pipes[i];
int from = pipe[0];
int to = pipe[1];
edgeList.add(Arrays.asList(from, to, pipe[2]));
edgeList.add(Arrays.asList(to, from, pipe[2]));
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
edgeList.add(Arrays.asList(0, i + 1, wells[i]));
edgeList.add(Arrays.asList(i + 1, 0, wells[i]));
}
PriorityQueue<List<Integer>> queue = new PriorityQueue<List<Integer>>((a, b) -> {
return a.get(2) - b.get(2);
});
for (List<Integer> edge: edgeList) {
queue.add(edge);
}
int cost = 0;
UF uf = new UF(100_000);
while (queue.size() > 0) {
List<Integer> edge = queue.poll();
int from = edge.get(0);
int to = edge.get(1);
if (!uf.isConnected(from, to)) {
uf.connect(from, to);
cost += edge.get(2);
}
}
return cost;
}
class UF {
int n;
int[] a;
int[] sizes;
public UF(int n) {
this.a = new int[n];
this.n = n;
this.sizes = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = i;
}
}
void connect(int p, int q) {
int pid = parent(p);
int qid = parent(q);
if (sizes[pid] > sizes[qid]) {
a[qid] = pid;
sizes[pid] += sizes[qid];
} else {
a[pid] = qid;
sizes[qid] += sizes[pid];
}
}
boolean isConnected(int i, int j) {
return parent(i) == parent(j);
}
int parent(int i) {
while (i != a[i]) {
i = a[i];
}
return i;
}
}
}
|
