Given a list of lists of integers, nums, return all elements of nums in diagonal order as shown in the below images.
Example 1:
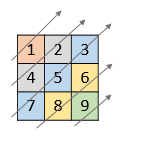
Input: nums = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [1,4,2,7,5,3,8,6,9]
Example 2:
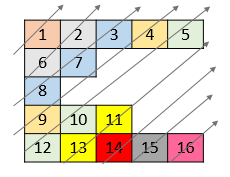
Input: nums = [[1,2,3,4,5],[6,7],[8],[9,10,11],[12,13,14,15,16]]
Output: [1,6,2,8,7,3,9,4,12,10,5,13,11,14,15,16]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [[1,2,3],[4],[5,6,7],[8],[9,10,11]]
Output: [1,4,2,5,3,8,6,9,7,10,11]
Example 4:
Input: nums = [[1,2,3,4,5,6]]
Output: [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 10^5
- 1 <= nums[i].length <= 10^5
- 1 <= nums[i][j] <= 10^9
- There at most 10^5 elements in nums.
Solution:
class Solution {
public int[] findDiagonalOrder(List<List<Integer>> nums) {
List<Tuple> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums.get(i).size(); j++) {
Tuple t = new Tuple();
t.sum = i + j;
t.row = i;
t.val = nums.get(i).get(j);
ans.add(t);
}
}
ans.sort((t1, t2) -> {
int s = Integer.compare(t1.sum, t2.sum);
if (s != 0) {
return s;
}
return - Integer.compare(t1.row, t2.row);
});
int[] result = new int[ans.size()];
int i = 0;
for (Tuple t : ans) {
result[i] = t.val;
i++;
}
return result;
}
static class Tuple {
int sum;
int row;
int val;
}
}