Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Example 1:
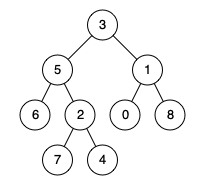
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
Output: 3
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.

Example 2:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
Output: 5
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2
Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [2, 105].
- -10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9
- All Node.val are unique.
- p != q
- p and q will exist in the tree.
Solution:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
List<TreeNode> parentNodes1 = new ArrayList();
List<TreeNode> parentNodes2 = new ArrayList();
search(root, p, parentNodes1);
search(root, q, parentNodes2);
int n = Math.min(parentNodes1.size(), parentNodes2.size());
TreeNode lca = root;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (parentNodes1.get(i).val == parentNodes2.get(i).val) {
lca = parentNodes1.get(i);
} else {
break;
}
}
return lca;
}
boolean search(TreeNode current, TreeNode target, List<TreeNode> path) {
if (current == null) return false;
path.add(current);
if (current.val == target.val) {
return true;
}
if (search(current.left, target, path)) {
return true;
}
if (search(current.right, target, path)) {
return true;
}
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
return false;
}
}
## Solution 2
```java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
List<TreeNode> path1 = new ArrayList<>();
search(root, p.val, path1);
List<TreeNode> path2 = new ArrayList<>();
search(root, q.val, path2);
for (int i = Math.min(path1.size(), path2.size()) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
var p1 = path1.get(i);
var p2 = path2.get(i);
if (p1.val == p2.val) return p1;
}
return null;
}
TreeNode search(TreeNode node, int val, List<TreeNode> paths) {
if (node == null) return null;
paths.add(node);
if (node.val == val) {
return node;
}
TreeNode s = search(node.left, val, paths);
if (s != null) return s;
s = search(node.right, val, paths);
if (s != null) return s;
paths.remove(node);
return null;
}
}
Solution 2021-11-18
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
Map<TreeNode, TreeNode> nodeParent = new HashMap<>();
stack.push(root);
nodeParent.put(root, null);
while (!nodeParent.containsKey(p) || !nodeParent.containsKey(q)) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if (node.right != null) {
nodeParent.put(node.right, node);
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
nodeParent.put(node.left, node);
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
Set<TreeNode> parents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
while (p != null) {
parents.add(p);
p = nodeParent.get(p);
}
while (q != null && !parents.contains(q)) {
q = nodeParent.get(q);
}
return q;
}
}
Solution 2022-01-29
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
Map<TreeNode, TreeNode> nodeParent = new HashMap<>();
nodeParent.put(root, null);
while (!nodeParent.containsKey(p) || !nodeParent.containsKey(q)) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if (node.right != null) {
nodeParent.put(node.right, node);
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
nodeParent.put(node.left, node);
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
Set<TreeNode> parents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 5
while (p != null) {
parents.add(p);
p = nodeParent.get(p);
}
while (q != null && !parents.contains(q)) {
q = nodeParent.get(q);
}
return q;
}
}