You have a graph of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given an integer n and a list of edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between nodes ai and bi in the graph.
Return true if the edges of the given graph make up a valid tree, and false otherwise.
Example 1:
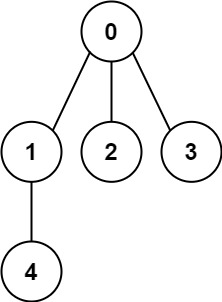
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,4]]
Output: true
Example 2:
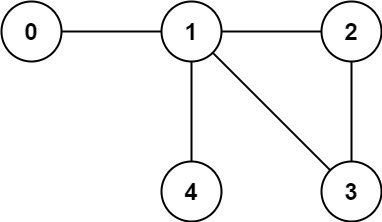
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[1,3],[1,4]]
Output: false
Constraints:
- 1 <= 2000 <= n
- 0 <= edges.length <= 5000
- edges[i].length == 2
- 0 <= ai, bi < n
- ai != bi
- There are no self-loops or repeated edges.
Solution
class Solution {
public boolean validTree(int n, int[][] edges) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.put(i, new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] edge: edges) {
int source = edge[0];
int target = edge[1];
graph.get(source).add(target);
graph.get(target).add(source);
}
// [ {1: 2,3,4}, {2: {5,6}}]
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
boolean hasCycles = dfs(0, -1, graph, visited);
if (hasCycles) {
return false;
}
for (boolean hasVisit: visited) {
if (!hasVisit) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
boolean dfs(int start, int prev, Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph, boolean[] visited) {
// already visited, has cycle
if (visited[start]) {
return true;
}
visited[start] = true;
for (Integer node: graph.get(start)) {
if (node == prev) continue;
boolean hasCycle = dfs(node, start, graph, visited);
if (hasCycle) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}